What if your body is sending signals you’ve overlooked? While many associate a missed period with potential pregnancy, subtle shifts like fatigue, nausea, or tender breasts often spark uncertainty. Recognizing these changes early can help you navigate next steps with clarity.
Every person’s experience differs. Some notice changes within days of conception, while others feel nothing for weeks. Hormonal fluctuations—like rising hCG levels—trigger physical responses, but timing and intensity vary widely.
A reliable pregnancy test remains the most accurate confirmation method. However, testing too soon can yield false results. Experts recommend waiting until at least one week after a missed cycle for precise readings.
This guide explores common indicators, from mild cramping to heightened sensitivity to smells. You’ll learn how to distinguish typical signs from false alarms and when to consult a healthcare provider. Let’s decode the clues your body might be sharing.
Introduction: Setting the Stage for Early Pregnancy Clarity
Could subtle shifts in your body hint at a life-changing event? Identifying initial signs promptly allows you to make informed decisions about prenatal care and lifestyle adjustments. Awareness empowers you to address nutritional needs, avoid harmful substances, and seek medical guidance early.
Understanding the Importance of Early Detection
Recognizing hormonal changes quickly supports both maternal well-being and fetal development. Studies show that early intervention reduces risks like nutrient deficiencies or exposure to toxins. Tracking methods—such as monitoring basal body temperature—help pinpoint conception timing with greater accuracy.
Overview of Common Indicators
Typical pregnancy symptoms include light spotting, nausea, and unusual fatigue. Breast tenderness often appears within days of conception due to rising progesterone levels. Food cravings or sudden aversions to familiar smells may also emerge as hormonal fluctuations intensify.
While these signs vary, combining symptom observation with at-home tests improves detection reliability. The following sections will break down each indicator, helping you distinguish meaningful changes from everyday bodily fluctuations.
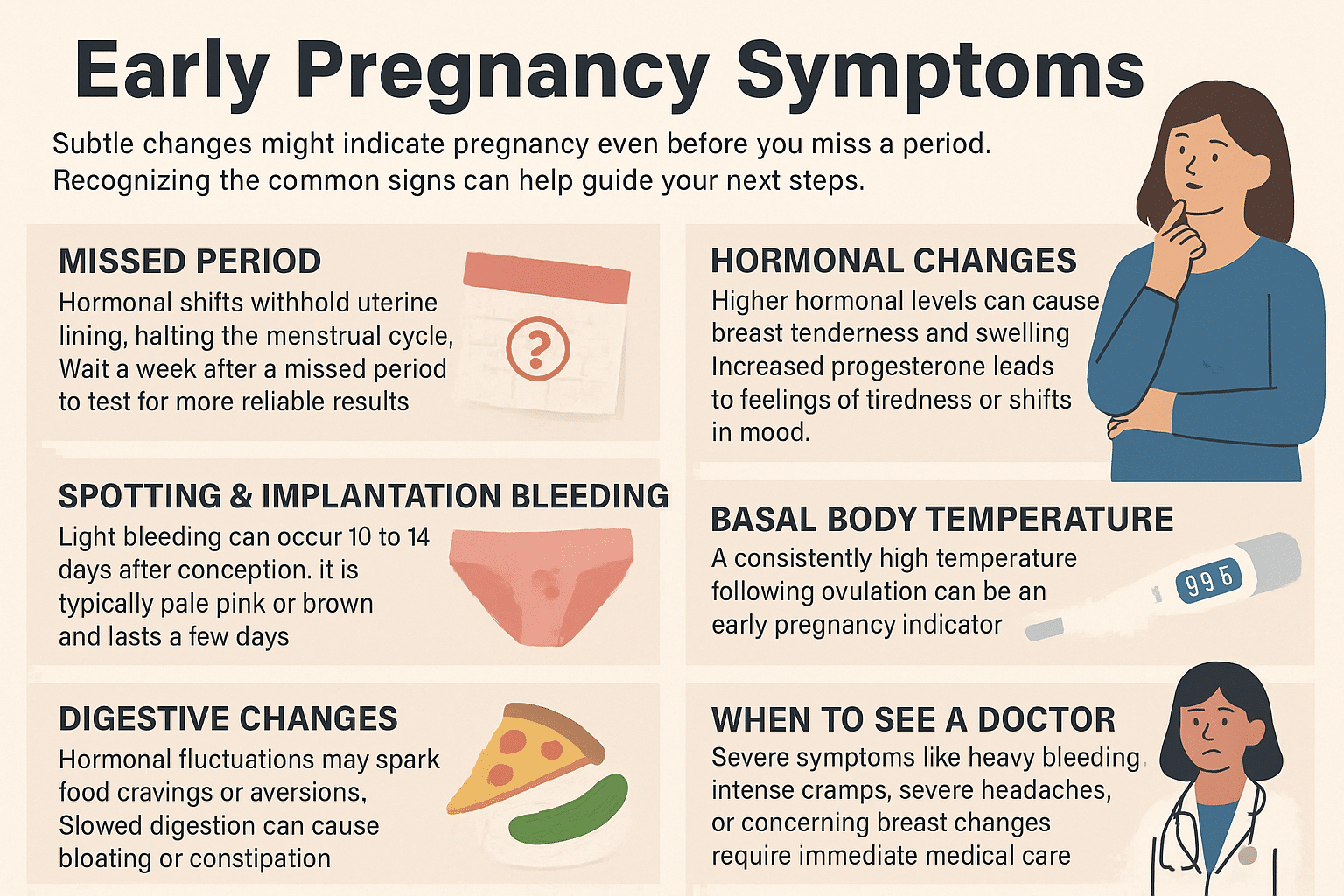
Recognizing a Missed Period as a Telling Early Sign
When your cycle skips its usual timing, it often sparks immediate questions. A missed period ranks among the most common initial signs noticed, occurring when conception prevents the shedding of uterine lining. This biological shift starts just days after fertilization, making it a critical early clue.
Hormones like hCG and progesterone surge during this phase. These chemical messengers signal your body to preserve the uterine environment rather than renew it monthly. Research shows 29% of people recognize this change before other symptoms appear, according to a 2023 clinical review.
How Hormonal Shifts Disrupt Your Cycle
Rising hCG levels confirm implantation, halting menstrual activity. Progesterone then maintains the uterine lining, creating ideal conditions for embryo development. This dual hormonal action explains why cycle interruptions often precede nausea or fatigue.
Testing too early can miss these changes. Most pregnancy tests detect hCG best one week after a missed period. For accurate results, wait until this window and use first-morning urine when hormone concentration peaks.
While irregular cycles can sometimes mimic this pattern, combining missed dates with other clues improves detection confidence. Track your cycle consistently to spot true deviations from your norm.
Spotting and Implantation Bleeding Explained
Light spotting often triggers confusion during early conception stages. Known as implantation bleeding, this occurs when the fertilized egg attaches to the uterine lining. Unlike menstrual flow, it typically appears as light pink or brown discharge and lasts 1-3 days.
Distinguishing Implantation Bleeding from Menstrual Flow
Color and flow intensity are key differentiators. Menstrual blood tends to start bright red and becomes heavier, while implantation spotting remains light with a pale hue. Cramps, if present, feel milder compared to period discomfort.
Timing matters most—implantation occurs 10-14 days after conception, often aligning with your expected cycle date. If bleeding coincides with this window and lacks clots, consider taking a pregnancy test a week later for clarity.
While light spotting usually isn’t concerning, consult a healthcare provider if you experience heavy flow, severe pain, or persistent bleeding. These could signal other conditions requiring attention. Track patterns using a symptom diary to share precise details during medical consultations.
Hormonal Changes and Their Impact on Your Body
Your body undergoes a silent transformation during conception’s earliest phases. Fluctuating estrogen and progesterone levels reshape physical sensations, often signaling adjustments before tests confirm results. These shifts prime your system to support new life while triggering noticeable responses.
Breast Tenderness and Swelling
Rising hormones boost blood flow to breast tissue, causing sensitivity within days of conception. Progesterone thickens milk ducts, while estrogen expands glandular structures. This dual action often creates persistent soreness distinct from typical premenstrual pain.
Increased Fatigue and Mood Shifts
Your body redirects energy to nurture embryonic growth, leaving you drained. Progesterone’s sedative-like effect amplifies exhaustion, especially during initial weeks. Simultaneously, hormonal surges can spark sudden emotional swings—tears one moment, joy the next—as neurotransmitters adapt to new chemical patterns.
Track these changes alongside your cycle. Symptoms lasting beyond two weeks or intensifying rapidly often differ from PMS. Consult your provider if discomfort disrupts daily routines or paired with unusual bleeding.
Tracking Basal Body Temperature and Cervical Changes
Your body whispers clues through temperature shifts and cervical patterns long before tests react. Tracking basal body temperature (BBT) offers a scientific window into conception timing. By measuring your morning temperature before rising, you can detect subtle post-ovulation changes caused by progesterone surges.
How Basal Body Temperature Signals Conception
A sustained BBT increase of 0.5-1°F for over 14 days often confirms pregnancy. This occurs because progesterone elevates your core temperature to support embryo development. Charting daily readings at the same morning hour sharpens accuracy—even small variations matter.
Cervical mucus transforms too. After ovulation, rising progesterone thickens discharge into a creamy or sticky texture. Some notice increased dryness, while others see milky-white secretions. These shifts create a protective barrier against bacteria during early stages.
Combine BBT charts with mucus observations for clearer insights. If temperatures stay high beyond your typical luteal phase, consider testing. Contact your doctor if patterns seem erratic or paired with severe nausea and vomiting—this could indicate hormonal imbalances needing attention.
Consistency is key. Use a digital thermometer designed for BBT tracking, and record data immediately upon waking. Fluctuations from illness or poor sleep may skew results, so note these factors. Your doctor can help interpret trends if you’ve tracked for multiple cycles without clear answers.
Digestive Shifts and Food Cravings: What to Look For
Have unexpected snack urges or sudden disgust for your morning coffee? Your gut might be reacting to hormonal shifts before a positive test appears. Progesterone—the key hormone supporting early development—slows digestion, creating noticeable physical signs like bloating or irregular bowel movements.
Understanding Bloating and Constipation
Rising progesterone relaxes intestinal muscles, causing food to move slower through your system. This creates a “traffic jam” effect, leading to abdominal pressure and constipation. Many report feeling fuller faster or experiencing mild cramps similar to menstrual discomfort.
Decoding Food Aversions and Cravings
Hormones also heighten smell and taste sensitivity. Suddenly hating your favorite meal? That’s your body’s way of steering you away from potential toxins. Conversely, intense food cravings—like pickles or citrus—may signal nutrient needs. Iron-rich meats and calcium-packed dairy often top the list.
Track these changes alongside other signs. Mild symptoms are normal, but persistent constipation paired with severe cramps warrants medical advice. Stay hydrated and add fiber-rich food to ease digestion while monitoring patterns.
When Severe Symptoms Mean It’s Time to See a Doctor
Not every change is a normal part of early development—some demand immediate attention. While mild cramping or fatigue often accompany conception, heavy blood flow or sharp pain signals urgency. Recognizing these differences helps protect both your health and potential outcomes.
Identifying Concerning Symptoms
Soaking through a pad in an hour with bright red blood or passing clots requires emergency care. Sudden, stabbing pelvic discomfort—unlike typical cramps—could indicate complications. Debilitating headaches paired with blurred vision may point to blood pressure issues needing swift intervention.
Breast changes like dimpling, sudden lumps, or bloody discharge also raise red flags. Symptoms lasting over a week without relief, such as relentless vomiting or fever above 102°F, should never be ignored.
Medical Advice and Next Steps
Contact your provider immediately if these signs appear. They’ll check blood pressure, hormone levels, and perform ultrasounds to assess viability. Early prenatal visits within 8 weeks help monitor fetal growth and address risks like ectopic pregnancy or infections.
Never self-diagnose severe headaches or unusual breast changes—timely professional evaluation ensures accurate solutions. Your care team can adjust medications, recommend tests, or provide treatments to support safer progression.
Early Pregnancy Symptoms: How to Tell If You’re Really Pregnant
Accurate testing bridges the gap between suspicion and certainty. Modern tests detect human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), a hormone produced after implantation. However, timing matters—testing too soon can miss low hCG levels, leading to false negatives. Research shows 25% of early tests produce inaccurate results due to improper time of use.
Why Precision Matters
Most tests reliably detect hCG one week after a missed cycle. Follow instructions carefully: first-morning urine contains concentrated hormone levels. Errors like early testing or diluted samples account for 80% of false readings, per a 2023 clinical study.
Symptoms like mood swings or morning sickness often align with detectable hCG levels. If you experience light discharge alongside these signs, wait 3-4 days before retesting. This timeframe allows hormone concentrations to rise above detection thresholds.
While home tests are 99% accurate when used correctly, consult a healthcare provider if results conflict with persistent mood changes or physical shifts. Confirming with a blood test eliminates doubts, ensuring you start prenatal care with clarity.
Comparing Early Pregnancy Signs with Premenstrual Indicators
Feeling drained and moody? Your body might be sending mixed signals. Premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and early conception share overlapping hormone-driven effects, but subtle differences in timing and intensity offer clues.
Fatigue appears in both scenarios but often feels more persistent with conception. While PMS exhaustion typically lifts after a few days, pregnancy-related tiredness may intensify over weeks as your body supports fetal growth.
Breast changes also differ. PMS causes temporary tenderness that fades post-cycle. Early pregnancy triggers fuller, heavier sensations due to hormone surges preparing milk ducts. Some notice darkened areolas—a change absent in typical PMS.
Mood swings can mislead you. Both conditions spark irritability, but pregnancy-related emotional shifts often last longer. A 2023 study found 68% of participants reported heightened sensitivity to smells alongside mood changes—a rare PMS occurrence.
Track symptom duration. PMS discomfort peaks 2-3 days before bleeding starts. Pregnancy signs like nausea or food aversions often escalate beyond this window. If symptoms persist 10+ days past your expected cycle, consider testing.
Your baby‘s development hinges on rising hormone levels, which amplify physical responses. Note patterns: consistent basal temperature spikes or unusual cervical mucus texture strengthen pregnancy suspicions. When in doubt, wait 5-7 days after missed bleeding for accurate test results.
Practical Tips for Monitoring and Confirming Your Pregnancy
Tracking your body’s signals requires precision and patience. Consistent observation helps distinguish meaningful patterns from random fluctuations. Start by charting your menstrual cycle length and physical changes—this baseline makes irregularities easier to spot.
When to Take a Pregnancy Test
For the most reliable result, wait 5-7 days after your missed cycle. Testing too early risks false negatives due to low hCG levels. First-morning urine offers concentrated hormone levels, improving accuracy.
If your cycle varies, track ovulation using basal body temperature. A sustained high reading for 14 consecutive days often confirms conception. Pair this data with cervical mucus changes—creamy textures post-ovulation may signal early developments.
Steps to Ensure a Healthy Start
Support your uterus environment with 400mcg of daily folic acid and iron-rich foods like spinach. Avoid alcohol and raw seafood to protect embryonic growth. Gentle exercises like walking improve blood flow to the uterus.
Use apps like Clue or Ovia to log symptoms, temperatures, and test results. Others find digital trackers simplify spotting trends. Share these records with your provider to assess uterine lining quality and hormone balance.
Proactive monitoring catches issues early. If tests conflict with symptoms after 10 days, request a blood test. A healthier uterus starts with informed choices—schedule your first prenatal visit within 8 weeks for optimal guidance.
Conclusion
What clues is your body sharing about potential changes? Missed cycles, fatigue, and nausea often point to hormones reshaping your system. Tracking these patterns—like breast tenderness or shifts in appetite—helps you act decisively during critical early stages.
Your body speaks through subtle cues. Sudden cravings for specific foods or aversions to familiar smells may signal nutrient needs. Documenting changes in energy levels or digestion creates a clearer picture when paired with reliable tests.
Always verify suspicions with clinical-grade tests after a missed cycle. While home kits provide initial answers, severe symptoms like heavy bleeding demand immediate professional evaluation. Understanding your unique rhythm helps distinguish normal fluctuations from meaningful shifts.
Knowledge transforms uncertainty into action. Trust your instincts while seeking expert guidance to confirm findings. By recognizing hormones‘ role in cravings and bodily changes, you empower informed choices for your well-being.


