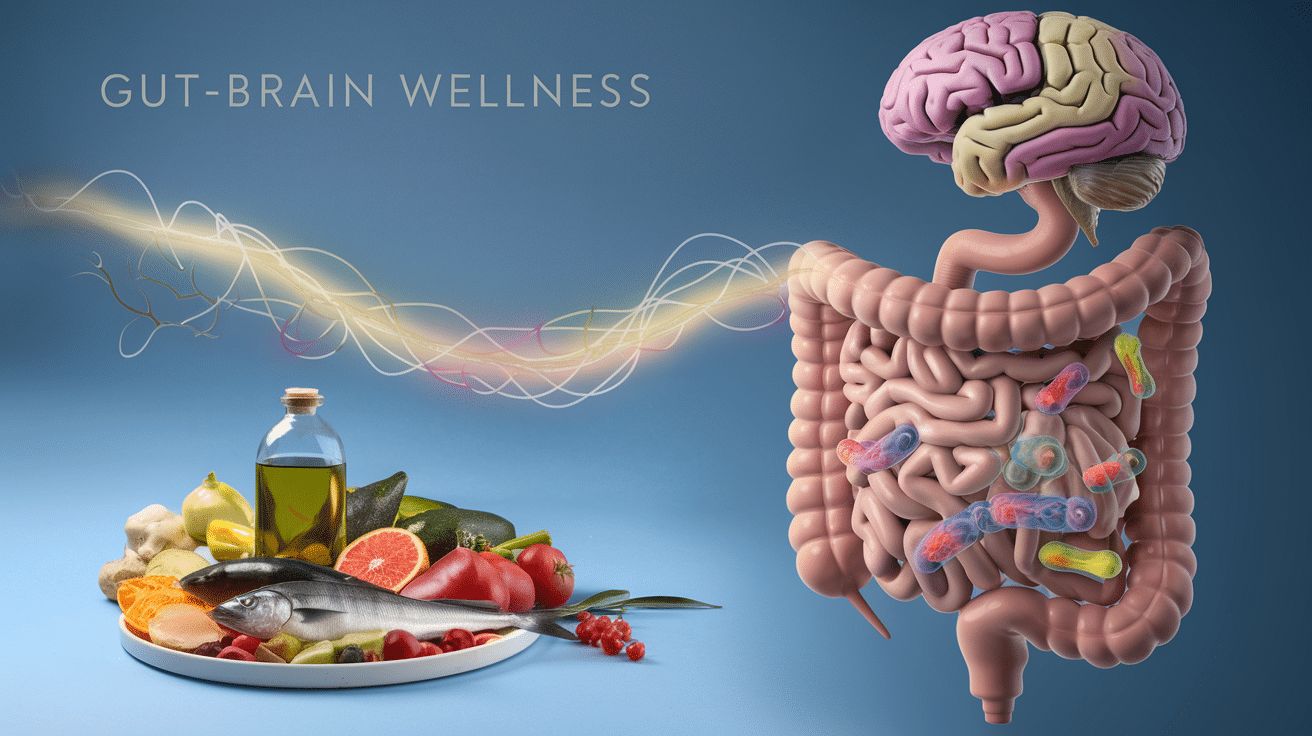
Have you ever felt butterflies in your stomach before a big presentation? Or experienced a “gut feeling” about a decision? These sensations aren’t just coincidences—they’re evidence of the powerful connection between your gut and your brain. 🦋🧠
The gut-brain link is a fascinating area of research that’s reshaping our understanding of mental health. Your digestive system isn’t just responsible for processing food; it plays a crucial role in your overall well-being, including your mood, cognitive function, and even your ability to handle stress. But here’s the kicker: when your gut health is compromised, it can have a ripple effect on your mental state, potentially leading to anxiety, depression, and other mood disorders.
In this blog post, we’ll dive deep into the intricate relationship between your gut and brain. You’ll discover why taking care of your digestive health is essential for maintaining optimal mental well-being. We’ll explore common digestive issues that can impact your mental health, reveal how to nurture your gut for better cognitive function, and uncover the powerful influence of diet and lifestyle on this vital connection. Get ready to transform your understanding of health and learn how to harness the gut-brain link for a happier, healthier you! 💪🥗
Understanding the Gut-Brain Connection
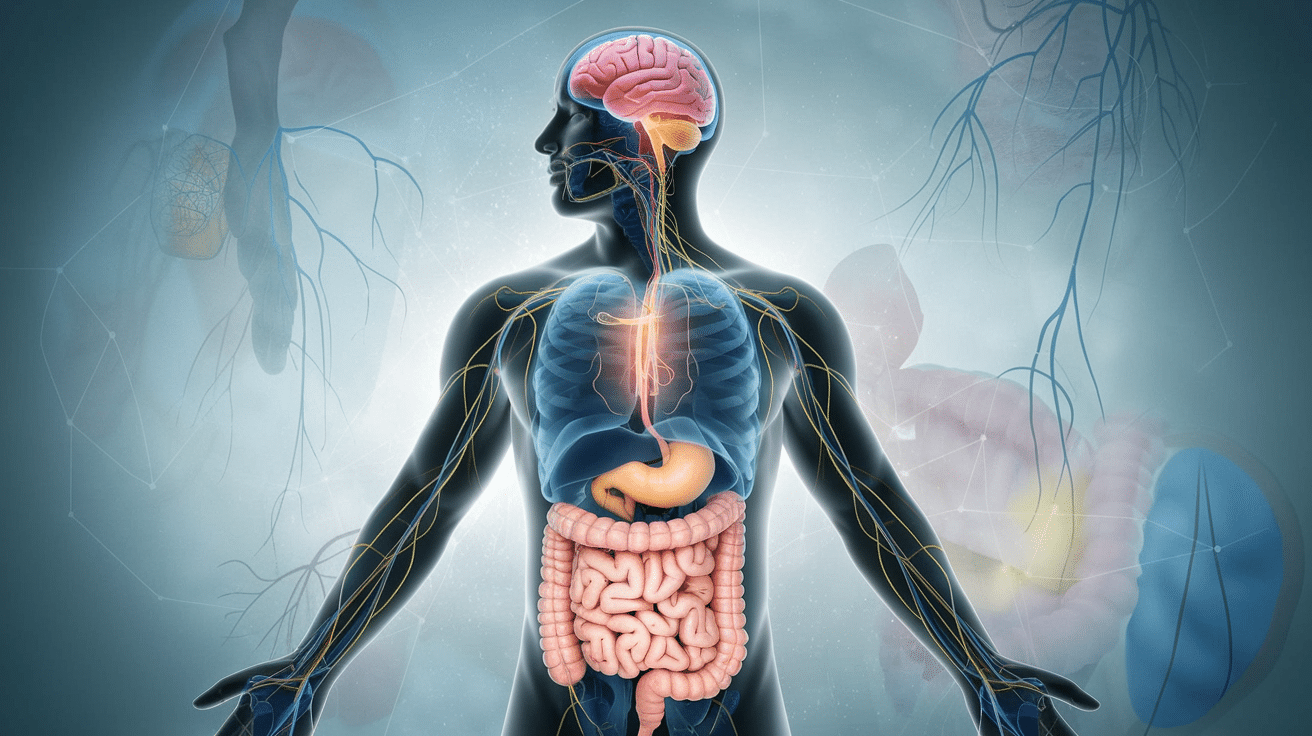
The Enteric Nervous System: Your Second Brain
You might be surprised to learn that your gut has its own nervous system, often referred to as your “second brain.” This complex network of neurons, called the enteric nervous system (ENS), lines your gastrointestinal tract and operates independently of your central nervous system.
The ENS is responsible for:
- Controlling digestion
- Regulating blood flow
- Managing the production of various gut hormones
Here’s a quick comparison of your two “brains”:
| Feature | Brain | Enteric Nervous System |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Skull | Gastrointestinal tract |
| Neuron count | 86 billion | 500 million |
| Primary function | Overall body control | Digestive regulation |
| Communication | Two-way with gut | Two-way with brain |
How Gut Microbiome Influences Mental Health
Your gut is home to trillions of microorganisms, collectively known as the gut microbiome. This diverse ecosystem plays a crucial role in your mental well-being. Here’s how:
- Neurotransmitter production: Gut bacteria produce neurotransmitters like serotonin and GABA.
- Immune system modulation: A healthy microbiome supports proper immune function, reducing inflammation that can affect mental health.
- Stress response regulation: Certain gut bacteria can help manage your body’s stress response.
The Role of Neurotransmitters in Gut-Brain Communication
Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that facilitate communication between your gut and brain. You may be surprised to learn that many of these are produced in your gut:
- Serotonin: 95% is produced in the gut, influencing mood and emotions
- Dopamine: Affects motivation and reward
- GABA: Helps regulate anxiety
Now that you understand the intricate connection between your gut and brain, let’s explore how common digestive issues can impact your mental well-being.
Common Digestive Issues Affecting Mental Well-being
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) and Anxiety
You may be surprised to learn that your digestive discomfort could be closely linked to your anxiety levels. IBS, a common gut disorder, often goes hand-in-hand with anxiety. Here’s what you need to know:
- Symptoms of IBS: Abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, constipation
- Anxiety symptoms: Excessive worry, restlessness, difficulty concentrating
The gut-brain connection plays a crucial role in this relationship. Your gut sends signals to your brain, and vice versa, creating a feedback loop that can exacerbate both IBS and anxiety symptoms.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Depression
If you’re dealing with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), such as Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis, you might also be at a higher risk for depression. Here’s a comparison of the two conditions:
| Aspect | IBD | Depression |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Symptoms | Abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss | Fatigue, changes in appetite |
| Emotional Impact | Stress, anxiety | Persistent sadness, loss of interest |
| Inflammation | In the gut | Potentially in the brain |
Gut Dysbiosis and Mood Disorders
Your gut microbiome plays a crucial role in your mental health. When the balance of good and bad bacteria in your gut is disrupted (dysbiosis), it can lead to various mood disorders. Here’s what you should be aware of:
- Dysbiosis can affect neurotransmitter production
- It may lead to increased inflammation throughout the body
- Mood disorders linked to dysbiosis include depression and anxiety
Food Intolerances and Cognitive Function
What you eat can significantly impact your cognitive function. If you have food intolerances, they might be affecting your brain health more than you realize. Common culprits include:
- Gluten
- Dairy
- Artificial additives
By identifying and eliminating problematic foods, you may experience improvements in memory, focus, and overall cognitive function.
Nurturing Your Gut for Better Mental Health
Probiotics: Beneficial Bacteria for Mind and Body
Probiotics are live microorganisms that can provide numerous health benefits when consumed in adequate amounts. These “good” bacteria play a crucial role in maintaining both your gut and mental health. Here’s how probiotics can positively impact your well-being:
- Improve mood and reduce anxiety
- Enhance cognitive function
- Boost immune system
- Reduce inflammation in the gut and brain
| Probiotic Strain | Mental Health Benefits |
|---|---|
| Lactobacillus | Reduces anxiety and depression |
| Bifidobacterium | Improves cognitive function |
| Saccharomyces | Alleviates stress-related symptoms |
Prebiotics: Feeding Your Gut’s Good Bacteria
Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that serve as food for the beneficial bacteria in your gut. By nourishing these microorganisms, you can enhance their ability to support your mental well-being. Some excellent sources of prebiotics include:
- Garlic
- Onions
- Asparagus
- Bananas
- Oats
Anti-inflammatory Foods for Gut and Brain Health
Reducing inflammation in both your gut and brain is crucial for maintaining optimal mental health. Incorporate these anti-inflammatory foods into your diet:
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel)
- Leafy greens (spinach, kale)
- Berries (blueberries, strawberries)
- Turmeric
- Olive oil
Stress Management Techniques for Digestive Balance
Stress can significantly impact your gut health, which in turn affects your mental well-being. Practice these stress-reduction techniques to maintain a healthy gut-brain connection:
- Mindfulness meditation
- Deep breathing exercises
- Regular physical activity
- Adequate sleep
- Yoga or tai chi
By implementing these strategies, you can nurture your gut health and positively influence your mental well-being. Remember, a healthy gut contributes to a healthier mind, so prioritize your digestive health as part of your overall wellness routine.
The Impact of Diet on Gut-Brain Health
The Mediterranean Diet: A Gut-Friendly Approach
The Mediterranean diet is not just good for your heart; it’s also excellent for your gut-brain health. This diet emphasizes:
- Whole grains
- Fresh fruits and vegetables
- Lean proteins (especially fish)
- Healthy fats (like olive oil)
- Limited processed foods
By focusing on these nutrient-rich foods, you’re providing your gut microbiome with the fuel it needs to thrive, which in turn supports your mental well-being.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Essential for Brain Function
Omega-3 fatty acids play a crucial role in brain health and gut-brain communication. Here’s why you should include them in your diet:
| Omega-3 Source | Brain Benefits | Gut Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Fatty fish | Improved cognitive function | Reduced gut inflammation |
| Walnuts | Enhanced mood stability | Supports gut barrier integrity |
| Flaxseeds | Better memory | Promotes beneficial gut bacteria |
Fiber-Rich Foods: Fuel for Gut Microbiome
Your gut microbiome thrives on fiber. By incorporating fiber-rich foods into your diet, you’re:
- Promoting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria
- Enhancing the production of short-chain fatty acids
- Improving gut barrier function
- Supporting regular bowel movements
These benefits collectively contribute to better mental health by reducing inflammation and improving nutrient absorption.
Limiting Processed Foods and Added Sugars
To maintain a healthy gut-brain connection, it’s crucial to limit your intake of processed foods and added sugars. These foods can:
- Disrupt the balance of your gut microbiome
- Increase inflammation in both your gut and brain
- Lead to mood swings and energy crashes
Instead, focus on whole, unprocessed foods to support your gut health and, consequently, your mental well-being. Remember, what’s good for your gut is often good for your brain!
Lifestyle Factors Influencing Gut and Mental Health
Regular Exercise: Boosting Gut and Brain Function
You’ve learned about the importance of diet, but physical activity plays a crucial role in maintaining both gut and brain health. Regular exercise can significantly improve your digestive function and mental well-being. Here’s how:
- Increased blood flow to the gut
- Enhanced diversity of gut microbiome
- Reduced stress and anxiety levels
- Improved mood and cognitive function
| Exercise Type | Gut Benefits | Brain Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Aerobic | Promotes healthy digestion | Boosts mood and reduces anxiety |
| Strength | Improves gut barrier function | Enhances cognitive performance |
| Yoga | Reduces gut inflammation | Decreases stress and promotes relaxation |
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week to reap these benefits. Remember, consistency is key!
Quality Sleep: Essential for Digestive and Mental Recovery
Your sleep habits have a profound impact on both your gut health and mental state. Quality sleep allows your body to repair and regenerate, including your digestive system and brain. Consider these sleep-improving strategies:
- Stick to a consistent sleep schedule
- Create a relaxing bedtime routine
- Avoid screens before bed
- Keep your bedroom cool and dark
Mindfulness and Meditation: Calming the Gut-Brain Axis
Practicing mindfulness and meditation can help you manage stress, which directly affects your gut-brain connection. By incorporating these techniques into your daily routine, you can:
- Reduce inflammation in the gut
- Lower cortisol levels
- Improve digestive function
- Enhance mental clarity and focus
Start with just 5-10 minutes of daily meditation and gradually increase the duration as you become more comfortable with the practice.
Your digestive health plays a crucial role in your overall well-being, including your mental health. The gut-brain connection is a powerful link that influences your mood, cognitive function, and emotional state. By addressing common digestive issues and nurturing your gut health, you can significantly improve your mental well-being.
Remember, the food you eat and your lifestyle choices have a direct impact on both your gut and brain health. By making mindful decisions about your diet and incorporating healthy habits into your daily routine, you can strengthen the gut-brain connection and promote better mental health. Take charge of your digestive health today, and you’ll be taking a significant step towards a happier, healthier mind.