Have you ever felt butterflies in your stomach when nervous or experienced a “gut feeling” about something? 🦋 These sensations aren’t just coincidences—they’re signs of the intricate connection between your gut and your brain. The relationship between gut health and mood is more profound than you might think, and it’s time to unveil the truth behind this fascinating link.
Imagine having the power to boost your mood, reduce anxiety, and improve your overall mental well-being, all by taking care of your gut. Sounds too good to be true? Well, it’s not! Recent scientific discoveries have shown that your gut health plays a crucial role in your emotional state. From the foods you eat to the stress you experience, everything impacts this delicate balance. But don’t worry—understanding and nurturing this connection can lead to transformative changes in both your physical and mental health.
In this blog post, we’ll dive deep into the gut-brain connection, exploring how your diet influences your mood, the impact of stress on your digestive system, and common gut issues that can affect your emotions. Most importantly, you’ll discover practical ways to improve your gut health and, in turn, enhance your mental well-being. So, are you ready to embark on a journey to a happier, healthier you? Let’s get started! 🌟
Understanding the Gut-Brain Connection
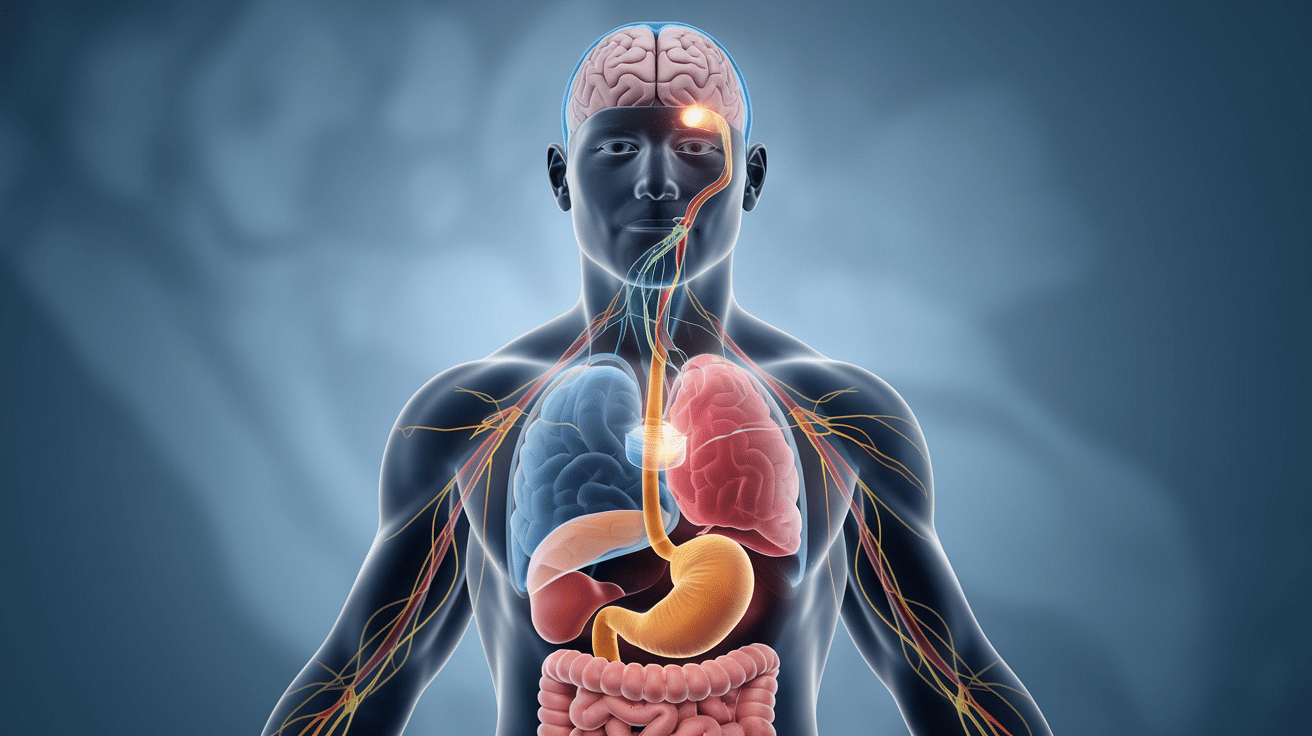
What is the gut-brain axis?
The gut-brain axis is a bidirectional communication system between your digestive tract and your central nervous system. This complex network involves neural, endocrine, and immune pathways that allow your gut and brain to “talk” to each other.
Here’s a breakdown of the key components:
- Vagus nerve: The primary neural connection
- Enteric nervous system: Your “second brain” in the gut
- Hormones: Chemical messengers that travel through the bloodstream
- Immune cells: Modulators of both gut and brain function
| Aspect | Function |
|---|---|
| Neural | Rapid signaling via nerves |
| Endocrine | Slower communication through hormones |
| Immune | Inflammation and protective responses |
How gut microbiota influences mood
Your gut microbiome plays a crucial role in modulating your mood and behavior. These tiny organisms can:
- Produce neurotransmitters like serotonin and GABA
- Influence stress responses and anxiety levels
- Affect cognitive function and memory
Research has shown that imbalances in gut bacteria can contribute to mood disorders such as depression and anxiety. Conversely, a healthy, diverse microbiome can promote emotional well-being.
The role of neurotransmitters in gut health
Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that play a vital role in both your gut and brain function. Surprisingly, many of these compounds are produced in your digestive system:
- Serotonin: 95% is produced in the gut
- GABA: Regulates anxiety and stress
- Dopamine: Influences motivation and reward
- Norepinephrine: Affects alertness and arousal
Your gut bacteria can directly influence the production and regulation of these neurotransmitters, impacting your mood and overall mental health. This intricate relationship underscores the importance of maintaining a healthy gut for optimal emotional well-being.
The Impact of Diet on Gut Health and Mood
Beneficial foods for gut health
Your gut health plays a crucial role in your overall well-being, including your mood. To support a healthy gut, incorporate these beneficial foods into your diet:
- Fermented foods: Kimchi, sauerkraut, kefir, and yogurt
- Fiber-rich vegetables: Broccoli, Brussels sprouts, and artichokes
- Whole grains: Quinoa, brown rice, and oats
- Lean proteins: Fish, poultry, and legumes
- Healthy fats: Avocados, olive oil, and nuts
Foods that may negatively affect gut health
While some foods nourish your gut, others can disrupt its delicate balance:
| Food Category | Examples | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Processed foods | Chips, cookies, frozen meals | Inflammation, imbalanced microbiome |
| Added sugars | Sodas, candies, sweetened cereals | Feeds harmful bacteria, promotes inflammation |
| Artificial sweeteners | Diet sodas, sugar-free gum | Alters gut bacteria composition |
| Excessive alcohol | Beer, wine, spirits | Damages gut lining, disrupts microbiome |
The importance of fiber and prebiotics
Fiber and prebiotics are essential for maintaining a healthy gut. They serve as food for beneficial gut bacteria, promoting their growth and activity. Aim for a diverse range of fiber-rich foods, including:
- Fruits: Apples, berries, and bananas
- Vegetables: Asparagus, garlic, and onions
- Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, and beans
- Whole grains: Barley, wheat bran, and flaxseeds
Probiotics and their effects on mood
Probiotics are live beneficial bacteria that can positively impact your gut health and, consequently, your mood. Research suggests that certain probiotic strains may help alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression. You can find probiotics in:
- Fermented dairy products (yogurt, kefir)
- Kombucha
- Miso
- Tempeh
By incorporating these gut-friendly foods into your diet and limiting those that may harm your gut health, you can support your digestive system and potentially improve your mood. Remember, a balanced diet rich in whole foods is key to maintaining a healthy gut-brain connection.
Stress and Its Effects on Gut Health
How stress impacts digestion
Stress can wreak havoc on your digestive system, affecting everything from nutrient absorption to bowel movements. When you’re under stress, your body enters a “fight or flight” mode, diverting blood flow away from your digestive organs. This can lead to:
- Decreased enzyme production
- Slowed digestion
- Increased stomach acid
- Inflammation in the gut lining
These effects can manifest as various digestive issues, including:
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Bloating | Feeling of fullness and discomfort |
| Nausea | Feeling sick to your stomach |
| Constipation | Difficulty passing stools |
| Diarrhea | Loose, watery stools |
The gut’s role in stress response
Your gut plays a crucial role in how your body responds to stress. The enteric nervous system, often called the “second brain,” communicates bidirectionally with your central nervous system. This gut-brain axis means that stress not only affects your gut but your gut also influences how you handle stress.
When you’re stressed, your gut:
- Produces stress hormones
- Alters the balance of gut bacteria
- Increases intestinal permeability (leaky gut)
- Affects neurotransmitter production
Stress management techniques for better gut health
To improve your gut health and manage stress, consider incorporating these techniques into your daily routine:
- Mindfulness meditation: Practice for 10-15 minutes daily to reduce stress hormones
- Deep breathing exercises: Use techniques like diaphragmatic breathing to activate your parasympathetic nervous system
- Regular exercise: Engage in moderate physical activity to boost mood and reduce inflammation
- Adequate sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep to support gut health and stress resilience
By managing your stress levels, you’re not only improving your mental well-being but also supporting a healthier gut. This, in turn, can lead to better overall health and mood regulation.
Common Gut Issues and Their Emotional Impact
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) and anxiety
You might be surprised to learn that your gut issues could be closely linked to your anxiety levels. Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a common digestive disorder that often goes hand-in-hand with anxiety. When you experience IBS symptoms like abdominal pain, bloating, and altered bowel habits, it can trigger feelings of worry and stress. Conversely, anxiety can exacerbate IBS symptoms, creating a vicious cycle.
Here’s a breakdown of the IBS-anxiety connection:
| IBS Impact on Anxiety | Anxiety Impact on IBS |
|---|---|
| Unpredictable symptoms cause worry | Stress triggers gut discomfort |
| Social isolation due to symptoms | Overthinking about symptoms |
| Fear of public embarrassment | Increased gut sensitivity |
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) and depression
If you’re dealing with Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD), such as Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis, you might also be at a higher risk for depression. The chronic nature of IBD can take a toll on your mental health, leading to feelings of hopelessness and sadness. Understanding this connection is crucial for managing both your gut health and emotional well-being.
Leaky gut syndrome and mood disorders
Leaky gut syndrome, while controversial in some medical circles, may play a role in various mood disorders. When your gut lining becomes more permeable, it can allow toxins and partially digested food particles to enter your bloodstream, potentially triggering inflammation throughout your body, including your brain.
To address these gut issues and their emotional impact, consider:
- Seeking professional help for both gut and mental health concerns
- Adopting a gut-friendly diet rich in fiber and probiotics
- Practicing stress-reduction techniques like meditation or yoga
- Staying physically active to boost both gut and mental health
Remember, your gut health and mood are intricately connected. By addressing one, you’re likely to see improvements in the other.
Improving Gut Health for Better Mental Well-being
Lifestyle changes to support gut health
To improve your gut health and mental well-being, consider implementing these lifestyle changes:
- Increase fiber intake
- Stay hydrated
- Reduce processed foods
- Manage stress levels
- Limit alcohol consumption
| Change | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Fiber-rich diet | Promotes healthy digestion and feeds beneficial gut bacteria |
| Hydration | Supports digestive processes and helps maintain gut lining |
| Whole foods | Provide essential nutrients for gut health and reduce inflammation |
| Stress management | Decreases negative impact on gut microbiome |
| Moderate alcohol | Prevents disruption of gut bacteria balance |
Mindful eating practices
Adopting mindful eating habits can significantly improve your gut health and mood. Pay attention to your food choices, eat slowly, and chew thoroughly. This practice allows your digestive system to work more efficiently and enhances nutrient absorption.
Exercise and its benefits for gut and mood
Regular physical activity is crucial for maintaining a healthy gut and improving your mood. Exercise stimulates the growth of diverse gut bacteria, which can positively influence your mental well-being. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
The role of sleep in gut health maintenance
Quality sleep is essential for optimal gut health and mood regulation. Establish a consistent sleep schedule and create a relaxing bedtime routine. Adequate sleep helps maintain a healthy gut microbiome balance and supports your body’s natural healing processes.
Now that you understand the importance of lifestyle changes, let’s explore some common gut issues and their emotional impact.
Your gut health plays a crucial role in your overall well-being, including your mood and mental state. By understanding the intricate connection between your gut and brain, you can take proactive steps to improve both your digestive and emotional health. Remember that a balanced diet, stress management, and addressing common gut issues are key factors in maintaining a healthy gut-brain axis.
Take charge of your gut health today to enhance your mood and mental well-being. Start by incorporating gut-friendly foods into your diet, practicing stress-reduction techniques, and seeking professional help if you experience persistent digestive or emotional issues. By nurturing your gut health, you’re not just taking care of your digestive system – you’re investing in your overall happiness and quality of life.